深層畳み込みニューラルネットワーク(その③)theanoとDeepLearningPython35のバージョンについて
たまたまgithubサイトを見ていて以下のコメントに気が付いた。

Avoid ImportError: cannot import name 'downsample'. New naming convention has been added in Theano 0.9 => use pool_2d instead
ImportErrorを避ける: 'downsample'という名前はインポートできません。 Theano 0.9で新しい命名規則が追加されました=>代わりにpool_2dを使用
とある。
修正されていたのか・・( ゚Д゚)
前回、前々回の
では、6月23日にダウンロードしたファイルでテストしていたのでエラーが生じていました・・・( ゚Д゚)。
さっそく 、以前(6月23日)にダウンロードした(DeepLearningPython35-master.zip)ファイルと、今回(11月5日)にダウンロードした(DeepLearningPython35-master.zip)ファイルをwinmergeで比較してみた。

Network3.pyファイル1つだけ修正されているみたいだ。
Network3.pyの変更箇所
42行目
from theano.tensor.signal import downsample
↓
from theano.tensor.signal.pool import pool_2d
230行目
pooled_out = downsample.max_pool_2d(
input=conv_out, ds=self.poolsize, ignore_border=True)↓
pooled_out = pool_2d(
input=conv_out, ws=self.poolsize, ignore_border=True)
"""network3.py ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ A Theano-based program for training and running simple neural networks. Supports several layer types (fully connected, convolutional, max pooling, softmax), and activation functions (sigmoid, tanh, and rectified linear units, with more easily added). When run on a CPU, this program is much faster than network.py and network2.py. However, unlike network.py and network2.py it can also be run on a GPU, which makes it faster still. Because the code is based on Theano, the code is different in many ways from network.py and network2.py. However, where possible I have tried to maintain consistency with the earlier programs. In particular, the API is similar to network2.py. Note that I have focused on making the code simple, easily readable, and easily modifiable. It is not optimized, and omits many desirable features. This program incorporates ideas from the Theano documentation on convolutional neural nets (notably, http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/lenet.html ), from Misha Denil's implementation of dropout (https://github.com/mdenil/dropout ), and from Chris Olah (http://colah.github.io ). """ #### Libraries # Standard library import pickle import gzip # Third-party libraries import numpy as np import theano import theano.tensor as T from theano.tensor.nnet import conv from theano.tensor.nnet import softmax from theano.tensor import shared_randomstreams from theano.tensor.signal.pool import pool_2d # Activation functions for neurons def linear(z): return z def ReLU(z): return T.maximum(0.0, z) from theano.tensor.nnet import sigmoid from theano.tensor import tanh #### Constants GPU = True if GPU: print("Trying to run under a GPU. If this is not desired, then modify "+\ "network3.py\nto set the GPU flag to False.") try: theano.config.device = 'gpu' except: pass # it's already set theano.config.floatX = 'float32' else: print("Running with a CPU. If this is not desired, then the modify "+\ "network3.py to set\nthe GPU flag to True.") #### Load the MNIST data def load_data_shared(filename="mnist.pkl.gz"): f = gzip.open(filename, 'rb') training_data, validation_data, test_data = pickle.load(f, encoding="latin1") f.close() def shared(data): """Place the data into shared variables. This allows Theano to copy the data to the GPU, if one is available. """ shared_x = theano.shared( np.asarray(data[0], dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=True) shared_y = theano.shared( np.asarray(data[1], dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=True) return shared_x, T.cast(shared_y, "int32") return [shared(training_data), shared(validation_data), shared(test_data)] #### Main class used to construct and train networks class Network(object): def __init__(self, layers, mini_batch_size): """Takes a list of `layers`, describing the network architecture, and a value for the `mini_batch_size` to be used during training by stochastic gradient descent. """ self.layers = layers self.mini_batch_size = mini_batch_size self.params = [param for layer in self.layers for param in layer.params] self.x = T.matrix("x") self.y = T.ivector("y") init_layer = self.layers[0] init_layer.set_inpt(self.x, self.x, self.mini_batch_size) for j in range(1, len(self.layers)): # xrange() was renamed to range() in Python 3. prev_layer, layer = self.layers[j-1], self.layers[j] layer.set_inpt( prev_layer.output, prev_layer.output_dropout, self.mini_batch_size) self.output = self.layers[-1].output self.output_dropout = self.layers[-1].output_dropout def SGD(self, training_data, epochs, mini_batch_size, eta, validation_data, test_data, lmbda=0.0): """Train the network using mini-batch stochastic gradient descent.""" training_x, training_y = training_data validation_x, validation_y = validation_data test_x, test_y = test_data # compute number of minibatches for training, validation and testing num_training_batches = int(size(training_data)/mini_batch_size) num_validation_batches = int(size(validation_data)/mini_batch_size) num_test_batches = int(size(test_data)/mini_batch_size) # define the (regularized) cost function, symbolic gradients, and updates l2_norm_squared = sum([(layer.w**2).sum() for layer in self.layers]) cost = self.layers[-1].cost(self)+\ 0.5*lmbda*l2_norm_squared/num_training_batches grads = T.grad(cost, self.params) updates = [(param, param-eta*grad) for param, grad in zip(self.params, grads)] # define functions to train a mini-batch, and to compute the # accuracy in validation and test mini-batches. i = T.lscalar() # mini-batch index train_mb = theano.function( [i], cost, updates=updates, givens={ self.x: training_x[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size], self.y: training_y[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size] }) validate_mb_accuracy = theano.function( [i], self.layers[-1].accuracy(self.y), givens={ self.x: validation_x[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size], self.y: validation_y[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size] }) test_mb_accuracy = theano.function( [i], self.layers[-1].accuracy(self.y), givens={ self.x: test_x[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size], self.y: test_y[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size] }) self.test_mb_predictions = theano.function( [i], self.layers[-1].y_out, givens={ self.x: test_x[i*self.mini_batch_size: (i+1)*self.mini_batch_size] }) # Do the actual training best_validation_accuracy = 0.0 for epoch in range(epochs): for minibatch_index in range(num_training_batches): iteration = num_training_batches*epoch+minibatch_index if iteration % 1000 == 0: print("Training mini-batch number {0}".format(iteration)) cost_ij = train_mb(minibatch_index) if (iteration+1) % num_training_batches == 0: validation_accuracy = np.mean( [validate_mb_accuracy(j) for j in range(num_validation_batches)]) print("Epoch {0}: validation accuracy {1:.2%}".format( epoch, validation_accuracy)) if validation_accuracy >= best_validation_accuracy: print("This is the best validation accuracy to date.") best_validation_accuracy = validation_accuracy best_iteration = iteration if test_data: test_accuracy = np.mean( [test_mb_accuracy(j) for j in range(num_test_batches)]) print('The corresponding test accuracy is {0:.2%}'.format( test_accuracy)) print("Finished training network.") print("Best validation accuracy of {0:.2%} obtained at iteration {1}".format( best_validation_accuracy, best_iteration)) print("Corresponding test accuracy of {0:.2%}".format(test_accuracy)) #### Define layer types class ConvPoolLayer(object): """Used to create a combination of a convolutional and a max-pooling layer. A more sophisticated implementation would separate the two, but for our purposes we'll always use them together, and it simplifies the code, so it makes sense to combine them. """ def __init__(self, filter_shape, image_shape, poolsize=(2, 2), activation_fn=sigmoid): """`filter_shape` is a tuple of length 4, whose entries are the number of filters, the number of input feature maps, the filter height, and the filter width. `image_shape` is a tuple of length 4, whose entries are the mini-batch size, the number of input feature maps, the image height, and the image width. `poolsize` is a tuple of length 2, whose entries are the y and x pooling sizes. """ self.filter_shape = filter_shape self.image_shape = image_shape self.poolsize = poolsize self.activation_fn=activation_fn # initialize weights and biases n_out = (filter_shape[0]*np.prod(filter_shape[2:])/np.prod(poolsize)) self.w = theano.shared( np.asarray( np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=np.sqrt(1.0/n_out), size=filter_shape), dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=True) self.b = theano.shared( np.asarray( np.random.normal(loc=0, scale=1.0, size=(filter_shape[0],)), dtype=theano.config.floatX), borrow=True) self.params = [self.w, self.b] def set_inpt(self, inpt, inpt_dropout, mini_batch_size): self.inpt = inpt.reshape(self.image_shape) conv_out = conv.conv2d( input=self.inpt, filters=self.w, filter_shape=self.filter_shape, image_shape=self.image_shape) pooled_out = pool_2d( input=conv_out, ws=self.poolsize, ignore_border=True) self.output = self.activation_fn( pooled_out + self.b.dimshuffle('x', 0, 'x', 'x')) self.output_dropout = self.output # no dropout in the convolutional layers class FullyConnectedLayer(object): def __init__(self, n_in, n_out, activation_fn=sigmoid, p_dropout=0.0): self.n_in = n_in self.n_out = n_out self.activation_fn = activation_fn self.p_dropout = p_dropout # Initialize weights and biases self.w = theano.shared( np.asarray( np.random.normal( loc=0.0, scale=np.sqrt(1.0/n_out), size=(n_in, n_out)), dtype=theano.config.floatX), name='w', borrow=True) self.b = theano.shared( np.asarray(np.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=(n_out,)), dtype=theano.config.floatX), name='b', borrow=True) self.params = [self.w, self.b] def set_inpt(self, inpt, inpt_dropout, mini_batch_size): self.inpt = inpt.reshape((mini_batch_size, self.n_in)) self.output = self.activation_fn( (1-self.p_dropout)*T.dot(self.inpt, self.w) + self.b) self.y_out = T.argmax(self.output, axis=1) self.inpt_dropout = dropout_layer( inpt_dropout.reshape((mini_batch_size, self.n_in)), self.p_dropout) self.output_dropout = self.activation_fn( T.dot(self.inpt_dropout, self.w) + self.b) def accuracy(self, y): "Return the accuracy for the mini-batch." return T.mean(T.eq(y, self.y_out)) class SoftmaxLayer(object): def __init__(self, n_in, n_out, p_dropout=0.0): self.n_in = n_in self.n_out = n_out self.p_dropout = p_dropout # Initialize weights and biases self.w = theano.shared( np.zeros((n_in, n_out), dtype=theano.config.floatX), name='w', borrow=True) self.b = theano.shared( np.zeros((n_out,), dtype=theano.config.floatX), name='b', borrow=True) self.params = [self.w, self.b] def set_inpt(self, inpt, inpt_dropout, mini_batch_size): self.inpt = inpt.reshape((mini_batch_size, self.n_in)) self.output = softmax((1-self.p_dropout)*T.dot(self.inpt, self.w) + self.b) self.y_out = T.argmax(self.output, axis=1) self.inpt_dropout = dropout_layer( inpt_dropout.reshape((mini_batch_size, self.n_in)), self.p_dropout) self.output_dropout = softmax(T.dot(self.inpt_dropout, self.w) + self.b) def cost(self, net): "Return the log-likelihood cost." return -T.mean(T.log(self.output_dropout)[T.arange(net.y.shape[0]), net.y]) def accuracy(self, y): "Return the accuracy for the mini-batch." return T.mean(T.eq(y, self.y_out)) #### Miscellanea def size(data): "Return the size of the dataset `data`." return data[0].get_value(borrow=True).shape[0] def dropout_layer(layer, p_dropout): srng = shared_randomstreams.RandomStreams( np.random.RandomState(0).randint(999999)) mask = srng.binomial(n=1, p=1-p_dropout, size=layer.shape) return layer*T.cast(mask, theano.config.floatX)
以上より、
theanoバージョン0.9とDeepLearningPython35-master.zipコミットが(Latest commit a8da42f on 28 Aug)であれば相性がよい。
ちなみに、theanoのバージョンを調べる場合は以下のようにする。
s:\plog\Python\python3\DeepLearningPython35-master>python -c "import theano; print(theano.__version__);"
(略)
0.9.0
気になること
Network3.pyの230行目の修正箇所で
input=conv_out, ds=self.poolsize, ignore_border=True)
input=conv_out, ws=self.poolsize, ignore_border=True)
ds=~が、ws=~に変わっていること。
あれ?、dsでなくてよいのだろうか?
そこで、theanoのライブラリpool.pyを見てみると
以下のようになっていた。
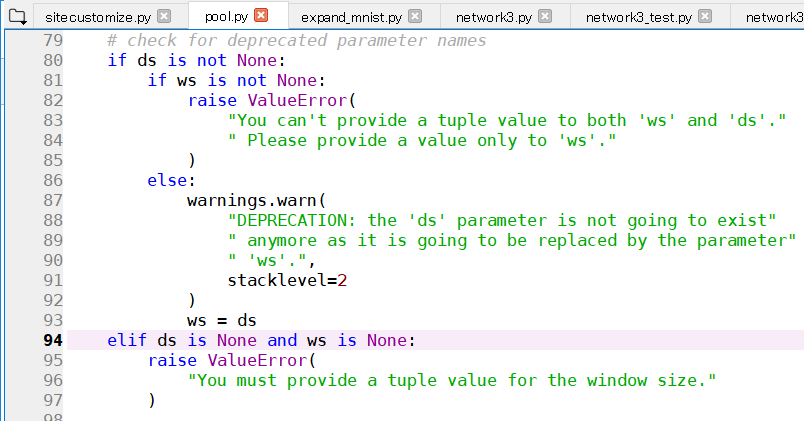
どうやら、dsで書かれた場合、ws = ds と、wsに差し替えられているので(ws,dsの記述はどちらでもよい)、最初からwsで記述しているみたいだ。( ゚Д゚)
それぞれの引数の説明を見ると
ws : tuple of length 2 or theano vector of ints of size 2.
Factor by which to downscale (vertical ws, horizontal ws).
(2,2) will halve the image in each dimension.ws:長さ2のタプル、またはサイズ2のintのベクトル。
ダウンスケーリングするファクタ(垂直ws、水平ws)。
(2,2)は各次元の画像を半分にします。ds
*deprecated*, use parameter ws instead.DS
* deprecated *、代わりにパラメータwsを使用します。
dsは、代わりにwsを使用すると書いてある。( ^ω^)・・・
多分、今まで、ds=~記述してあるソースを生かす為に、
削除せずにわざわざ残したんだね。
以上。